
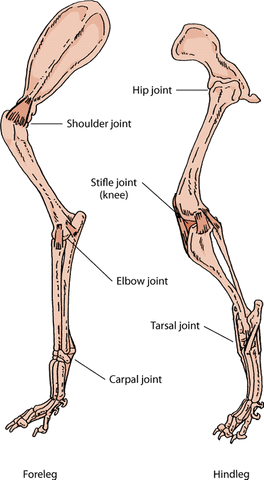
Three main nerves begin together at the shoulder the radial nerve, the ulnar nerve and the medial nerve. These two tendons are important to understand because they are common locations of tendonitis.Īll of the nerves that travel down the arm pass across the elbow. Most of the muscles that straighten the fingers and wrist come together and attach to the medial epicondyle, or the bump on the inside of your arm just above the elbow. The outside (lateral) bump just above the elbow is called the lateral epicondyle. join bone to bone, binding the skeleton together in a passive fashion. The muscles in your forearm cross the elbow and attach to the humerus. concentrate the force of a muscle onto a relatively small area of the skeleton. The important tendons of the elbow are the biceps tendon, which is attached the biceps muscle on the front of your arm, and the triceps tendon, which attaches the triceps muscle on the back of your arm. There are tendons in your elbow that attach muscle to bone. A third ligament, the annular ligament, holds the radial head tight against the ulna. The important ligaments of the elbow are the medial collateral ligament (on the inside of the elbow) and the lateral collateral ligament (on the outside of the elbow.) Together these ligaments provide the main source of stability for the elbow, holding the humerus and the ulna tightly together. The joint capsule is a fluid filled sac that surrounds and lubricates the joint. The bones are held together with ligaments that form the joint capsule. Cartilage has a rubbery consistency that allows the joints to slide easily against one another and absorb shock. The ends of the bones are covered with cartilage. The bones in a saddle joint can rock back and forth and from side to side, but they have limited rotation.The elbow is a hinged joint made up of three bones, the humerus, ulna, and radius.
The only saddle joints in your body are in your thumbs.Our hand bones are held in place and supported by various soft tissues. The pivot joint in your neck allows you to turn your head from side to side. The hands enable us to perform many of our daily activities such as driving.Hinge joints, like in your knee and elbow, enable movement similar to the opening and closing of a hinged door.Some of the bones in your wrists and ankles move by gliding against each other. Gliding joints occur between the surfaces of two flat bones that are held together by ligaments.It is lighter, less dense, and more flexible than compact. Ellipsoidal joints, such as the joint at the base of your index finger, allow bending and extending, rocking from side to side, but rotation is limited. Cancellous (trabecular or spongy) bone makes up the remaining 20 of bone and consists of a network of trabeculae, or rod-like, structures.They allow you to swing your arms and legs in many different directions. Ball and socket joints, like your hip and shoulder joints, are the most mobile type of joint in the human body. ligament, tough fibrous band of connective tissue that serves to support the internal organs and hold bones together in proper articulation at the joints.

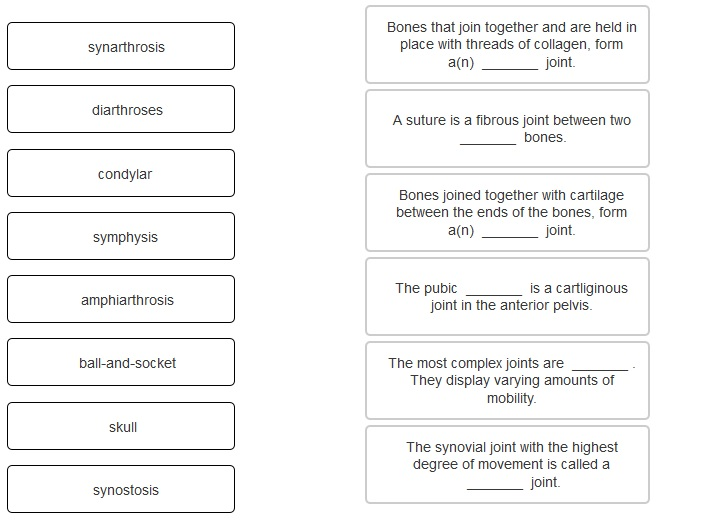
The most common synovial joints are listed below: Fibrous joints are found in the skull, which is made up of several bone plates held tightly together to protect the fragile brain. This tough connection allows very little movement between the joined bones, thus providing great stability. Ligaments help provide their stability and muscles contract to produce movement. Fibrous joints are held together by strong connective tissue with only a slight capacity to stretch. Synovial joints are predominant in your limbs where mobility is important. They are movable joints containing a lubricating liquid called synovial fluid. Most of your joints are 'synovial joints'. Other joints, such as those between the vertebrae in your spine, which are connected to each other by pads of cartilage, can only move a small amount. The bones in your skull are held together with fibrous connective tissue. Some of your joints, like those in your skull, are fixed and don't allow any movement. Joints hold your bones together and allow your rigid skeleton to move. The bones are held together at the joints by elastic strands. The places where this happens are called joints. All of your bones, except for one (the hyoid bone in your neck), form a joint with another bone. Bones are connected together so they can move. Joints are the place where two bones meet. Saddle joints: Enable you to grasp things Flexibility: Joints enable your body to moveīall and socket joints: Are the most mobile type of joint in your body


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
